Chlorine trifluoride (CLF3) electron geometry is a captivating area of study that explores the molecular structure of this unique compound. CLF3, with its intricate electron arrangement, plays a critical role in unraveling the complexities of chemical bonding and molecular geometry. By diving into the electron geometry of CLF3, we can gain deeper insights into its physical and chemical characteristics, making it an engaging topic for both students and professionals in the field of chemistry.
For those new to the concept, electron geometry refers to the three-dimensional configuration of electron pairs around a central atom in a molecule. In the case of CLF3, this arrangement has a profound impact on its behavior and reactivity. This article aims to provide a thorough explanation of CLF3 electron geometry, ensuring readers develop a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating subject.
Whether you're a student eager to learn, a researcher seeking insights, or someone with a general interest in chemistry, this guide will serve as an invaluable resource. We’ll delve into the intricacies of CLF3 electron geometry, its implications, and its connection to broader chemical principles. Let’s begin!
Read also:Exploring The Tickle Community Vk A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Exploring CLF3 Electron Geometry
- Molecular Structure of CLF3
- Applying VSEPR Theory to CLF3
- Bond Angles in CLF3
- Electron Pair Arrangement in CLF3
- Properties of CLF3
- Applications of CLF3
- Comparison with Other Compounds
- Common Questions about CLF3 Electron Geometry
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Exploring CLF3 Electron Geometry
Chlorine trifluoride (CLF3) is a compound made up of one chlorine atom and three fluorine atoms. Its electron geometry is determined by the spatial arrangement of electron pairs around the central chlorine atom. Understanding this geometry is crucial for predicting how the compound behaves in various chemical reactions and environments.
Why Electron Geometry Matters
The study of electron geometry is pivotal in determining the shape of molecules, which in turn influences their polarity, reactivity, and other physical properties. For CLF3, its electron geometry provides critical insights into how this compound interacts with other substances. Moreover, electron geometry plays a significant role in the compound's stability and its ability to participate in chemical reactions. This knowledge is particularly valuable in industries such as aerospace and electronics, where CLF3 is utilized as a cleaning agent and etchant.
Molecular Structure of CLF3
The molecular structure of CLF3 is shaped by its electron geometry. In this compound, the central chlorine atom is bonded to three fluorine atoms and has two lone pairs of electrons. This specific arrangement leads to a T-shaped molecular geometry, which is a direct result of the interactions between bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons.
Key Factors Influencing Molecular Structure
Several factors contribute to the molecular structure of CLF3, including:
- Electron repulsion: The repulsion between bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons significantly affects the geometry of the molecule.
- Number of electron domains: The total number of electron domains around the central atom determines the initial electron geometry before considering lone pairs.
- Hybridization: The hybridization of the central atom plays a crucial role in shaping the molecule, as it dictates how the orbitals combine to form bonds.
These factors work together to define the overall shape and properties of CLF3, making it a unique and intriguing subject for scientific investigation.
Applying VSEPR Theory to CLF3
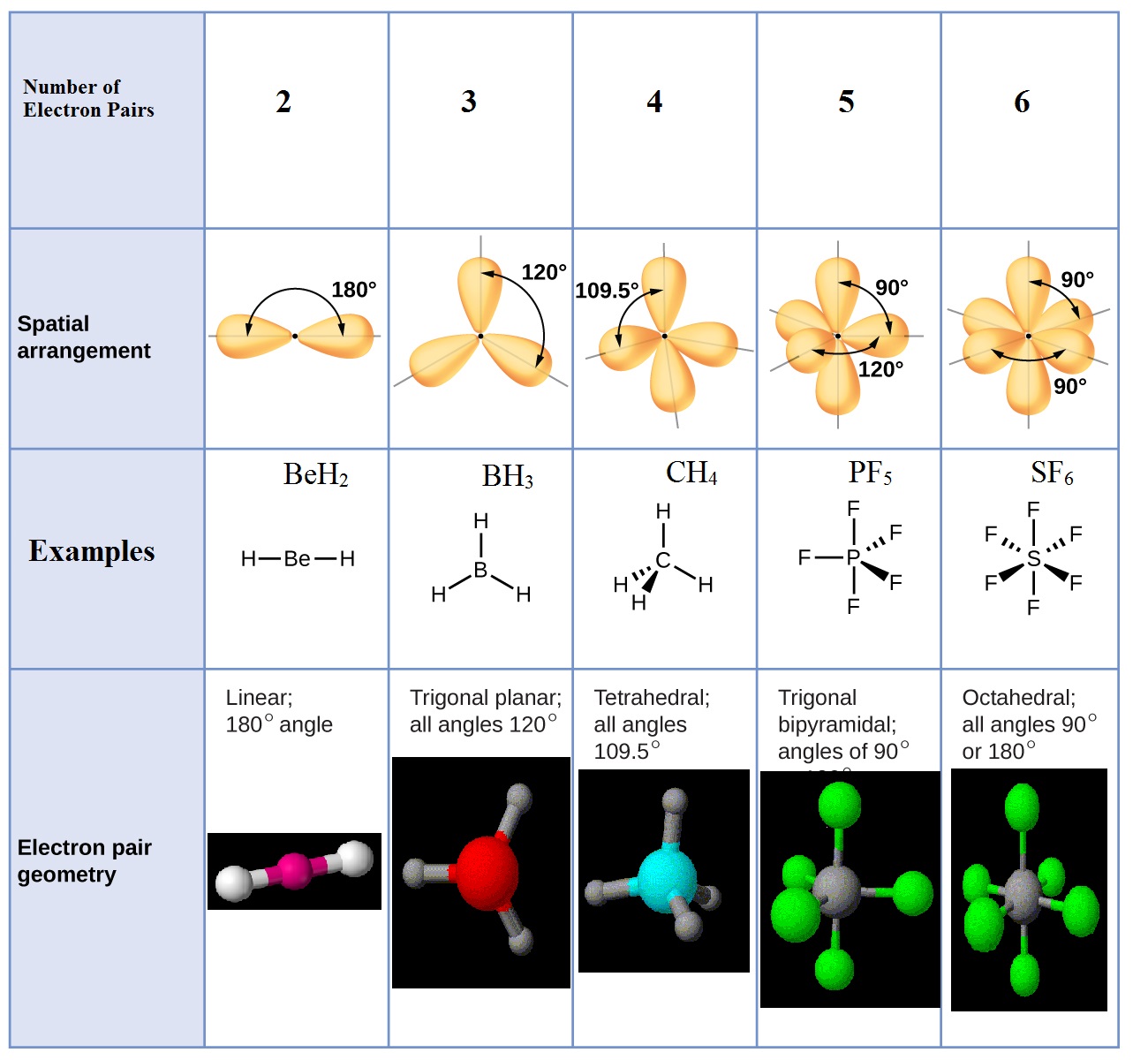
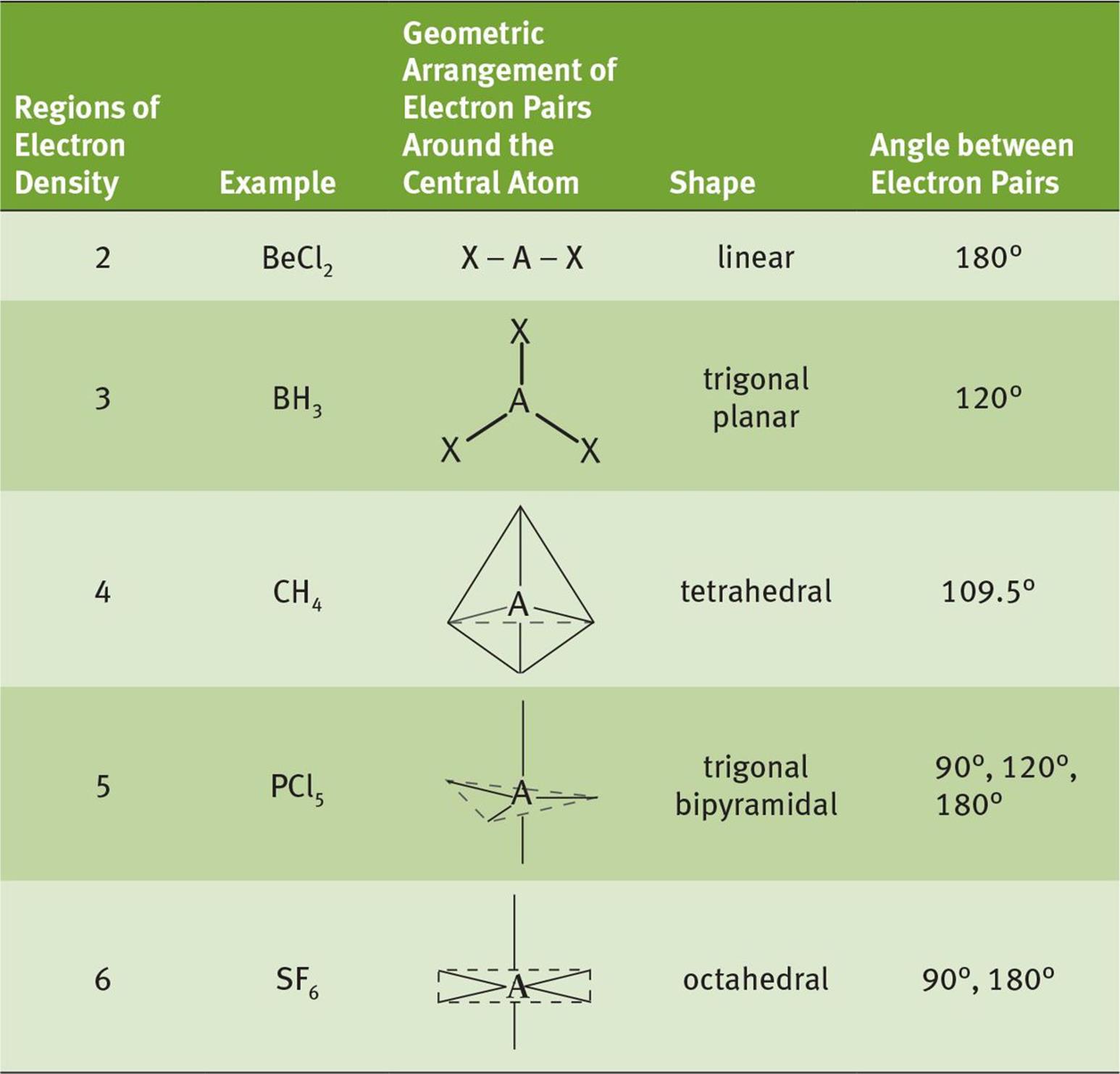
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a powerful tool used to predict the geometry of molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs. When applied to CLF3, VSEPR theory reveals its T-shaped geometry, which arises from the repulsion between the five electron domains surrounding the central chlorine atom. This includes three bonding pairs and two lone pairs.
Read also:Otogibanashio Onigokko A Comprehensive Guide To The Iconic Japanese Folklore Game
Steps to Apply VSEPR Theory
To apply VSEPR theory to CLF3 effectively, follow these steps:
- Determine the Lewis structure: Begin by drawing the Lewis structure of the molecule to identify the number of valence electrons and bonding pairs.
- Identify electron domains: Count the total number of electron domains around the central atom, including both bonding pairs and lone pairs.
- Predict electron geometry: Use the number of domains to predict the initial electron geometry before accounting for lone pairs.
- Determine molecular geometry: Consider the presence of lone pairs to refine the molecular geometry, as lone pairs occupy more space and cause distortions in the shape.
By following these steps, we can accurately predict the geometry of CLF3 and gain a deeper understanding of its unique properties.
Bond Angles in CLF3
The bond angles in CLF3 are influenced by the repulsion between electron pairs. In a T-shaped geometry, the bond angles between the fluorine atoms are approximately 90 degrees and 180 degrees. However, these angles are slightly distorted due to the greater repulsion exerted by lone pairs compared to bonding pairs.
Factors Influencing Bond Angles
Several factors contribute to the bond angles in CLF3, including:
- Electron pair repulsion: Lone pairs and bonding pairs repel each other, causing distortions in the bond angles.
- Hybridization: The hybridization of the central atom affects the spatial arrangement of orbitals, which in turn influences bond angles.
- Size and electronegativity: The size and electronegativity of the surrounding atoms also play a role in determining the exact bond angles.
Understanding these factors is essential for accurately predicting the geometry and properties of CLF3, as well as similar molecules.
Electron Pair Arrangement in CLF3
The electron pair arrangement in CLF3 is determined by VSEPR theory. The central chlorine atom has five electron domains, consisting of three bonding pairs and two lone pairs. This arrangement results in a trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry, which is distorted into a T-shaped molecular geometry due to the influence of the lone pairs.
Significance of Electron Pair Arrangement
The arrangement of electron pairs has a profound impact on the properties of CLF3. It affects the compound's polarity, reactivity, and overall stability. By comprehending the electron pair arrangement, chemists can better predict how CLF3 will behave in various chemical environments, making it easier to design experiments and applications involving this compound.
Properties of CLF3
CLF3 possesses several distinctive properties that make it valuable for a variety of applications. Some of these properties include:
- Polarity: CLF3 is a polar molecule due to its asymmetrical shape and the difference in electronegativity between chlorine and fluorine atoms.
- Reactivity: CLF3 is highly reactive and can react violently with water and other substances, making it both powerful and potentially dangerous.
- Toxicity: The compound is toxic and requires careful handling in industrial and laboratory settings to ensure safety.
These properties highlight the dual nature of CLF3 as both a powerful tool and a hazardous substance, emphasizing the importance of proper safety measures during its use.
Applications of CLF3
Despite its reactivity and toxicity, CLF3 finds practical applications in several industries. Some of its key uses include:
- Aerospace: CLF3 is employed as a cleaning agent for rocket engines and other high-temperature components due to its strong oxidizing properties.
- Electronics: In the semiconductor industry, the compound serves as an etchant for cleaning and etching silicon wafers with precision.
- Research: CLF3 is utilized in research labs to study chemical reactions and molecular structures, contributing to advancements in chemistry and related fields.
Its unique combination of properties makes CLF3 indispensable in these fields, despite the challenges associated with its handling.
Comparison with Other Compounds
Comparing CLF3 with other compounds offers valuable insights into its distinctive characteristics. For instance, while both CLF3 and BF3 contain three fluorine atoms, their electron geometries differ significantly due to the presence of lone pairs in CLF3. This difference leads to contrasting properties and applications for each compound.
Notable Differences
Some key differences between CLF3 and other compounds include:
- Molecular geometry: CLF3 exhibits a T-shaped geometry, while BF3 has a trigonal planar geometry.
- Polarity: CLF3 is polar due to its asymmetrical shape, whereas BF3 is nonpolar.
- Reactivity: CLF3 is highly reactive, while BF3 is relatively inert under normal conditions.
Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate compound for specific applications and optimizing their use in various industries.
Common Questions about CLF3 Electron Geometry
Many questions arise when studying CLF3 electron geometry. Below are some frequently asked questions and their answers:
What is the electron geometry of CLF3?
The electron geometry of CLF3 is trigonal bipyramidal, while its molecular geometry is T-shaped due to the presence of two lone pairs on the central chlorine atom.
Why is CLF3 highly reactive?
CLF3 is highly reactive because of its strong oxidizing and fluorinating properties, which enable it to react with a wide range of substances, including metals, nonmetals, and even water.
Is CLF3 polar or nonpolar?
CLF3 is a polar molecule due to its asymmetrical shape and the significant difference in electronegativity between chlorine and fluorine atoms.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In summary, CLF3 electron geometry is a captivating area of study that provides profound insights into the world of chemistry. By understanding the molecular structure, properties, and applications of CLF3, we can appreciate its significance in various industries and research fields. However, its reactivity and toxicity necessitate careful handling to ensure safety in its use.
We encourage readers to engage with this content by leaving comments, sharing this article, or exploring other resources on our site to expand their knowledge of chemistry. Together, let’s continue to uncover the wonders of the chemical world!
For further reading, consider consulting authoritative sources such as the Journal of Chemical Education and the American Chemical Society for additional insights into CLF3 and related compounds.