Grasping the distinction between centripetal and centrifugal forces is vital for anyone delving into physics or engineering. These forces are integral to numerous natural processes and technological innovations. By exploring their definitions, characteristics, and practical examples, we can develop a profound understanding of how they shape the motion of objects in our world.
In the field of physics, forces serve as the catalysts behind the movement of objects. From the motion of celestial bodies to the operation of thrilling amusement park rides, and the stability of vehicles navigating curves, centripetal and centrifugal forces are at play. This article will delve into these forces in detail, offering a clear differentiation between them and their roles in the universe.
Our exploration will focus on explaining the foundational principles, practical applications, and real-world scenarios where these forces are observed. Whether you're a student, educator, or simply an enthusiast curious about the mechanics of motion, this article aims to be an invaluable resource for your understanding.
Read also:Maroon 5 Leinger A Comprehensive Guide To The Bands Iconic Song
Understanding Centripetal Force
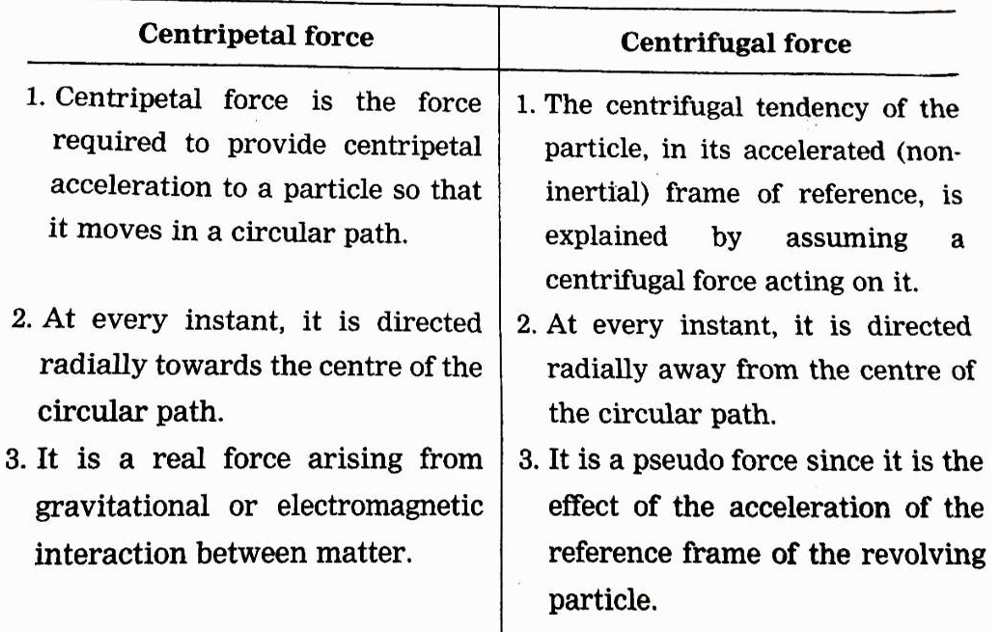
Centripetal force is the force that acts on an object moving along a circular path, pulling it toward the center of the circle. Without this inward force, the object would continue in a straight line due to inertia, as described by Newton's first law of motion. This force is consistently directed perpendicular to the motion of the object and toward the fixed center point of the circular path, ensuring the object follows its curved trajectory.
Here are some key aspects of centripetal force:
- Direction: It always acts toward the center of the circular motion.
- Magnitude: It is calculated using the formula \( F = \frac{mv^2}{r} \), where \( F \) represents the force, \( m \) is the mass of the object, \( v \) is the velocity, and \( r \) is the radius of the circular path.
- Examples: Common sources of centripetal force include tension in a string, gravitational pull, and frictional forces.
Exploring Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force is commonly misunderstood as a force that acts outward from the center of a circular path. However, it is a fictitious or pseudo-force that arises in a rotating reference frame. It gives the impression of pushing objects away from the center of rotation, but it does not exist as a real force in an inertial reference frame.
Centrifugal force originates from the inertia of an object and is perceived when analyzing motion from a non-inertial frame of reference. For instance, when you're in a car taking a sharp turn, the sensation of being pushed outward is due to centrifugal force, which is a result of your body's resistance to the change in direction.
Comparing Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
While both forces are associated with circular motion, they differ significantly in their nature and effects. Below is an in-depth comparison:
- Type: Centripetal force is a genuine force, while centrifugal force is a fictitious one.
- Direction: Centripetal force acts toward the center, whereas centrifugal force appears to act outward.
- Frame of Reference: Centripetal force is observed in an inertial frame, whereas centrifugal force is experienced in a non-inertial frame.
Mathematical Representation of Both Forces
The mathematical representation of centripetal and centrifugal forces allows us to quantitatively understand their behavior. The formula for centripetal force is:
Read also:Natalie Portman The Iconic Journey Of A Hollywood Star
\( F_c = \frac{mv^2}{r} \)
Where:
- \( F_c \): Centripetal force
- \( m \): Mass of the object
- \( v \): Velocity of the object
- \( r \): Radius of the circular path
Centrifugal force, being a fictitious force, does not have a standalone formula but is mathematically equivalent in magnitude to centripetal force when observed from a rotating frame:
\( F_{cf} = \frac{mv^2}{r} \)
Practical Applications of Centripetal Force
Centripetal force is evident in a variety of real-world situations. Below are some examples:
- Planetary Motion: Gravitational force acts as the centripetal force that keeps planets orbiting around the sun in a stable path.
- Banked Roads: Roads are designed with a slight incline at curves to provide the necessary centripetal force, ensuring vehicles can navigate safely without skidding.
- Amusement Park Rides: Popular rides such as the Ferris wheel and roller coasters rely on centripetal force to keep passengers securely moving along curved paths, enhancing their thrill.
Practical Applications of Centrifugal Force
Though centrifugal force is fictitious, it has tangible applications in various fields:
- Washing Machines: The spin cycle in washing machines utilizes centrifugal force to effectively remove water from clothes, improving efficiency.
- Centrifuges: These devices employ centrifugal force to separate substances based on their densities, which is critical in scientific and medical laboratories.
- Artificial Gravity: In space exploration, centrifugal force is used to simulate gravity in rotating habitats, providing astronauts with a more stable environment.
Addressing Misconceptions About Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
There are several misconceptions surrounding these forces that need clarification. Below are some common ones:
- Centrifugal Force is Real: Many mistakenly believe centrifugal force is a real force, but it is, in fact, a fictitious force experienced only in non-inertial frames.
- Opposite Forces: Centripetal and centrifugal forces are not opposing forces; they function within different reference frames and contexts.
- Centripetal Force Cancels Out: Centripetal force does not negate centrifugal force; they coexist but are relevant in distinct scenarios.
Historical Evolution of the Concept
The concepts of centripetal and centrifugal forces have developed over centuries through the contributions of influential scientists. Isaac Newton was instrumental in formally describing centripetal force in his laws of motion. Subsequently, the concept of centrifugal force was introduced to explain motion in non-inertial frames, further enriching our understanding.
These ideas have been continuously refined and expanded by physicists, leading to a more comprehensive comprehension of motion and its underlying principles.
Newton's Role in Centripetal Force
Newton's groundbreaking work on centripetal force formed the cornerstone of classical mechanics. He demonstrated that the force necessary to maintain an object in circular motion is always directed toward the center. This principle is essential for comprehending planetary motion and other natural phenomena.
Interactive Demonstrations
Several experiments can effectively illustrate the effects of centripetal and centrifugal forces. For instance, swinging a ball attached to a string in a circular motion demonstrates centripetal force. Similarly, using a rotating platform can simulate centrifugal force, providing a tangible experience of its effects.
Engaging in these hands-on experiments allows students and enthusiasts to better grasp these concepts, bridging the gap between theory and practice.
Final Thoughts
In summary, understanding the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces is essential for grasping the mechanics of circular motion. Centripetal force is a real force that acts toward the center of a circular path, while centrifugal force is a fictitious force perceived in a rotating reference frame. Both forces have significant applications in daily life and scientific research.
We encourage you to expand your knowledge by conducting your own experiments or exploring related articles. If you have any questions or insights, feel free to share them in the comments below. Additionally, don't hesitate to share this article with others who may find it enlightening!
Table of Contents
- Understanding Centripetal Force
- Exploring Centrifugal Force
- Comparing Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
- Mathematical Representation of Both Forces
- Practical Applications of Centripetal Force
- Practical Applications of Centrifugal Force
- Addressing Misconceptions About Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
- Historical Evolution of the Concept
- Interactive Demonstrations
- Final Thoughts