In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become a cornerstone for businesses seeking to enhance their operational efficiency and innovation. As more devices become interconnected, the need for secure and scalable cloud infrastructure has grown exponentially. In this context, IoT Virtual Private Cloud (IoT VPC) and Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) have emerged as critical solutions. But what exactly are these technologies, and how do they differ from one another?
IoT Virtual Private Cloud and VPC are both designed to provide a secure environment for storing and processing data. However, their applications and capabilities vary significantly, especially when it comes to IoT-specific use cases. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses that want to make informed decisions about their cloud infrastructure.
This article will delve into the nuances of IoT Virtual Private Cloud vs VPC, exploring their features, benefits, and limitations. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of which solution best suits your business needs.
Read also:Naughty America The Ultimate Guide To Exploring The World Of Adult Entertainment
Table of Contents
- Introduction to IoT Virtual Private Cloud and VPC
- What is IoT Virtual Private Cloud?
- What is Virtual Private Cloud?
- IoT Virtual Private Cloud vs VPC: Key Differences
- Security Features of IoT VPC and VPC
- Scalability in IoT VPC and VPC
- Cost Considerations for IoT VPC and VPC
- Use Cases for IoT Virtual Private Cloud and VPC
- Implementation Steps for IoT VPC and VPC
- Future Trends in IoT VPC and VPC
- Conclusion and Recommendations
Introduction to IoT Virtual Private Cloud and VPC
As the number of connected devices continues to grow, the demand for secure and scalable cloud solutions has never been higher. Both IoT Virtual Private Cloud (IoT VPC) and Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) play vital roles in this domain. IoT VPC is specifically tailored for IoT applications, offering enhanced security and performance for device-to-cloud communication. On the other hand, VPC provides a general-purpose private cloud environment suitable for a wide range of applications.
The primary goal of both solutions is to isolate resources within a public cloud environment, ensuring data privacy and security. However, their specific features and capabilities cater to different needs. For instance, IoT VPC focuses on optimizing communication between IoT devices and cloud services, while VPC offers broader flexibility for diverse workloads.
Understanding the distinctions between IoT Virtual Private Cloud vs VPC is essential for businesses aiming to leverage the full potential of cloud computing. This article will explore these differences in depth, helping you make an informed decision.
What is IoT Virtual Private Cloud?
An IoT Virtual Private Cloud is a specialized cloud infrastructure designed explicitly for IoT applications. It provides a secure and isolated environment for IoT devices to communicate with cloud services. IoT VPC ensures that sensitive data transmitted between devices and the cloud remains protected from unauthorized access.
Key Features of IoT Virtual Private Cloud
- Enhanced Security: IoT VPC employs advanced encryption and authentication mechanisms to safeguard data.
- Scalability: It can handle large volumes of data generated by IoT devices, ensuring seamless performance even as the number of devices grows.
- Low Latency: IoT VPC is optimized for real-time data processing, reducing latency in device-to-cloud communication.
- Integration: It seamlessly integrates with other cloud services, enabling businesses to build comprehensive IoT solutions.
According to a report by Gartner, the global IoT market is expected to reach $1.1 trillion by 2023. This growth underscores the importance of IoT VPC in supporting the expanding ecosystem of connected devices.
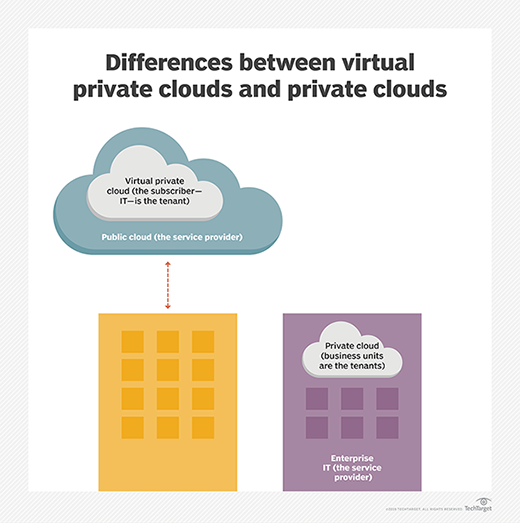
What is Virtual Private Cloud?
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a private cloud environment hosted within a public cloud infrastructure. It allows businesses to create isolated networks, ensuring data privacy and security. VPC is widely used for a variety of applications, from web hosting to enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
Read also:Louisa Khovanski Unveiling The Inspiring Story Of A Rising Star
Key Features of Virtual Private Cloud
- Network Isolation: VPC provides a dedicated network environment, protecting resources from other tenants in the public cloud.
- Customizable Subnets: Users can define their own IP address ranges and create subnets to organize resources efficiently.
- Access Control: VPC offers granular control over who can access specific resources, enhancing security.
- Interconnectivity: It supports both private and public connections, enabling businesses to connect their VPC to on-premises data centers.
VPC has become a cornerstone for businesses seeking to adopt cloud computing while maintaining control over their data. According to AWS, over 90% of Fortune 500 companies use VPC to manage their cloud resources.
IoT Virtual Private Cloud vs VPC: Key Differences
While both IoT Virtual Private Cloud and VPC offer secure cloud environments, they differ significantly in terms of their focus and capabilities. Below are some key distinctions:
1. Purpose
- IoT VPC: Specifically designed for IoT applications, focusing on device-to-cloud communication.
- VPC: A general-purpose private cloud environment suitable for a wide range of applications.
2. Security
- IoT VPC: Offers enhanced security features tailored for IoT devices, such as device authentication and encryption.
- VPC: Provides robust security mechanisms but is not specifically optimized for IoT use cases.
3. Scalability
- IoT VPC: Optimized for handling large volumes of data generated by IoT devices.
- VPC: Scalable but may require additional configuration for IoT-specific workloads.
These differences highlight the importance of selecting the right solution based on your business needs. For IoT-focused applications, IoT VPC is often the better choice.
Security Features of IoT VPC and VPC
Security is a top priority for both IoT Virtual Private Cloud and VPC. However, their approaches to securing data differ based on their intended use cases.
IoT Virtual Private Cloud Security
- Device Authentication: IoT VPC employs robust authentication mechanisms to ensure only authorized devices can access the cloud.
- Data Encryption: It uses end-to-end encryption to protect data both in transit and at rest.
- Network Isolation: IoT VPC isolates IoT devices from other resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Virtual Private Cloud Security
- Firewall Rules: VPC allows users to define custom firewall rules to control inbound and outbound traffic.
- IPSec Tunnels: It supports IPsec tunnels for secure communication between on-premises and cloud environments.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): VPC provides ACLs to regulate access to specific resources within the network.
Both solutions offer strong security features, but IoT VPC's specialized focus on IoT devices makes it the preferred choice for IoT applications.
Scalability in IoT VPC and VPC
Scalability is a critical factor when choosing between IoT Virtual Private Cloud and VPC. Both solutions are designed to handle growing workloads, but their scalability features differ in certain aspects.
IoT Virtual Private Cloud Scalability
- Automatic Scaling: IoT VPC can automatically scale resources based on the number of connected devices and data volume.
- Load Balancing: It supports load balancing to distribute traffic evenly across servers, ensuring optimal performance.
- Integration with IoT Platforms: IoT VPC integrates seamlessly with IoT platforms, enabling businesses to scale their solutions efficiently.
Virtual Private Cloud Scalability
- Manual Configuration: VPC requires manual configuration for scaling resources, which can be time-consuming for IoT-specific workloads.
- Multi-AZ Deployment: It supports multi-AZ deployment for high availability and fault tolerance.
- Customizable Resources: VPC allows users to customize resources to meet their specific scalability needs.
For businesses with rapidly growing IoT ecosystems, IoT VPC's automatic scaling capabilities make it the more practical choice.
Cost Considerations for IoT VPC and VPC
Cost is another important factor when evaluating IoT Virtual Private Cloud vs VPC. While both solutions offer competitive pricing, their cost structures differ based on usage patterns and resource requirements.
IoT Virtual Private Cloud Cost
- Pricing Model: IoT VPC often uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where businesses only pay for the resources they consume.
- Device Management Fees: Additional fees may apply for device management and monitoring services.
- Integration Costs: Businesses may incur costs for integrating IoT VPC with existing systems and platforms.
Virtual Private Cloud Cost
- Subscription Plans: VPC typically offers subscription-based pricing, with varying tiers based on resource usage.
- Network Charges: Businesses may be charged for data transfer and network usage within the VPC.
- Support Fees: Optional support services may incur additional costs, depending on the provider.
Businesses should carefully evaluate their usage patterns and resource requirements to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Use Cases for IoT Virtual Private Cloud and VPC
The choice between IoT Virtual Private Cloud and VPC often depends on the specific use case. Below are some common scenarios where each solution excels:
IoT Virtual Private Cloud Use Cases
- Smart Cities: IoT VPC is ideal for managing the vast network of sensors and devices in smart city applications.
- Industrial IoT: It supports real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Healthcare IoT: IoT VPC ensures secure and reliable communication between medical devices and cloud services.
Virtual Private Cloud Use Cases
- Web Hosting: VPC is widely used for hosting websites and web applications, providing a secure and scalable environment.
- Enterprise Applications: It supports enterprise-level applications, such as ERP and CRM systems, with high performance and reliability.
- Data Analytics: VPC is suitable for data analytics workloads, enabling businesses to process and analyze large datasets efficiently.
Selecting the right solution depends on the specific requirements of your use case. IoT VPC is ideal for IoT-focused applications, while VPC offers broader flexibility for diverse workloads.
Implementation Steps for IoT VPC and VPC
Implementing either IoT Virtual Private Cloud or VPC involves several key steps. Below is a general guide to help you get started:
IoT Virtual Private Cloud Implementation
- Define Requirements: Identify the specific needs of your IoT application, including the number of devices and expected data volume.
- Select a Provider: Choose a cloud provider that offers IoT VPC services, such as AWS IoT Core or Google Cloud IoT Core.
- Configure Resources: Set up the necessary resources, including subnets, security groups, and access policies.
- Integrate Devices: Connect your IoT devices to the cloud using the provider's APIs and SDKs.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor performance and optimize resources to ensure optimal efficiency.
Virtual Private Cloud Implementation
- Plan Your Network: Design your VPC architecture, including subnets, IP ranges, and routing tables.
- Choose a Provider: Select a cloud provider that offers VPC services, such as AWS VPC or Azure Virtual Network.
- Set Up Resources: Configure resources such as instances, storage, and databases within your VPC.
- Secure Your Environment: Implement security measures, including firewalls, ACLs, and encryption.
- Test and Deploy: Test your VPC setup thoroughly before deploying it into production.
Following these steps will help ensure a successful implementation of either IoT VPC or VPC.
Future Trends in