The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as one of the most transformative technologies of the 21st century, fundamentally altering the way we interact with the world around us. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT is revolutionizing industries and improving everyday life. This groundbreaking technology connects devices, enabling them to share data and automate processes, ultimately enhancing efficiency and convenience. As IoT continues to evolve, its impact on society is becoming increasingly profound.
IoT technology is no longer a futuristic concept but a reality that is shaping our present and future. It is transforming industries such as healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation, among others. By leveraging IoT, businesses can optimize operations, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences. Moreover, consumers benefit from smarter and more connected devices that enhance their quality of life.
However, the rapid growth of IoT also brings challenges, particularly in terms of security, privacy, and standardization. As the number of connected devices continues to rise, ensuring the safety and reliability of IoT systems becomes paramount. In this article, we will delve into the world of IoT, exploring its benefits, challenges, and future prospects, while providing actionable insights for businesses and individuals alike.
Read also:Stop Running Woo Lotti A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Taking Control
Table of Contents
- What is IoT?
- History of IoT
- Key Components of IoT
- Applications of IoT
- Benefits of IoT
- Challenges of IoT
- IoT Security
- IoT Privacy
- Future Trends in IoT
- Conclusion
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that can communicate and exchange data without human intervention. These devices, often embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enable them to collect and transmit information to other devices or systems. IoT technology spans a wide range of applications, from consumer products like smart thermostats and wearable devices to industrial solutions such as predictive maintenance and smart agriculture.
Definition of IoT
At its core, IoT is about connecting everyday objects to the internet, enabling them to send and receive data. This connectivity allows for automation, remote control, and real-time monitoring, making processes more efficient and convenient. For example, a smart refrigerator can notify you when you're running low on groceries or adjust its temperature based on the contents inside.
Examples of IoT Devices
- Smart Home Devices: Smart thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras.
- Wearable Technology: Fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitors.
- Industrial IoT: Sensors for predictive maintenance, smart grids, and supply chain management.
History of IoT
The concept of IoT has been evolving for decades, with its roots tracing back to the early days of computing. The term "Internet of Things" was first coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999, but the technology itself has been developing much longer. The evolution of IoT can be attributed to advancements in wireless communication, sensor technology, and cloud computing.
Milestones in IoT Development
- 1980s: Early experiments with connected devices, such as the Carnegie Mellon University Coke machine.
- 1990s: Introduction of RFID technology, which laid the foundation for modern IoT.
- 2000s: Rapid growth of wireless networks and the proliferation of smartphones, enabling widespread adoption of IoT.
Key Components of IoT
IoT systems consist of several key components that work together to enable connectivity and data exchange. Understanding these components is essential for grasping how IoT operates and its potential applications.
Sensors and Actuators
Sensors are devices that detect and measure physical properties, such as temperature, humidity, or motion, and convert them into digital data. Actuators, on the other hand, perform actions based on the data received, such as turning on a light or adjusting a thermostat.
Connectivity
Connectivity is the backbone of IoT, enabling devices to communicate with each other and the internet. Various communication protocols, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks, are used to establish connections between devices.
Read also:Emory Tate Height A Comprehensive Look Into The Life And Career Of A Chess Legend
Data Processing and Analytics
Once data is collected, it needs to be processed and analyzed to extract meaningful insights. This is where cloud computing and artificial intelligence come into play, allowing for real-time data analysis and decision-making.
Applications of IoT
The applications of IoT are vast and varied, spanning multiple industries and sectors. From enhancing consumer experiences to optimizing industrial processes, IoT is transforming the way we live and work.
Smart Homes
Smart home technology allows homeowners to control and automate various aspects of their living environment, such as lighting, climate control, and security systems. This not only improves convenience but also reduces energy consumption and costs.
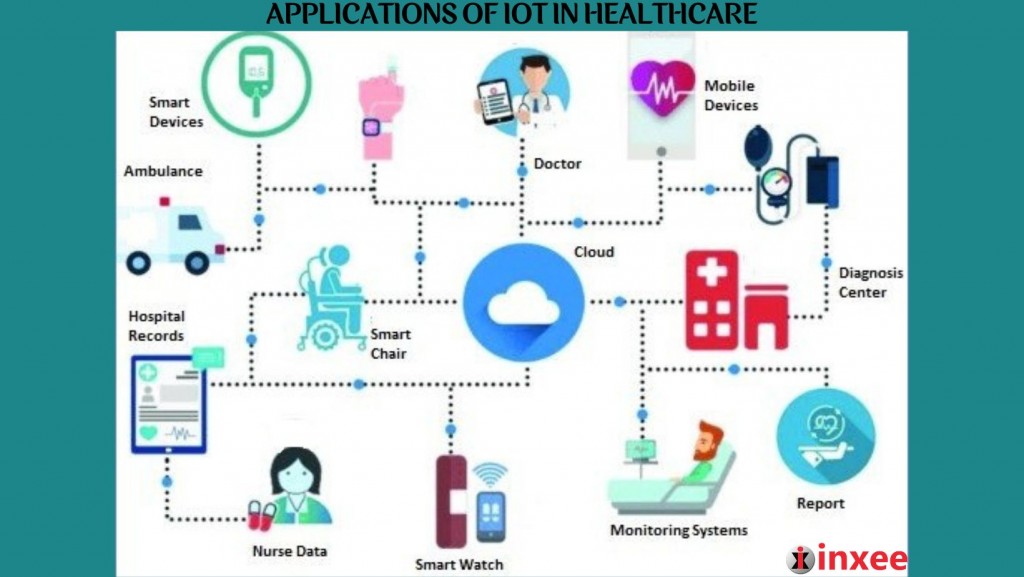
Healthcare
In healthcare, IoT is revolutionizing patient care through wearable devices, remote monitoring, and telemedicine. These innovations enable healthcare providers to deliver more personalized and efficient care, while patients benefit from improved health outcomes.
Manufacturing
IoT is transforming the manufacturing industry by enabling predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and supply chain optimization. This leads to increased productivity, reduced downtime, and improved quality control.
Benefits of IoT
The adoption of IoT offers numerous benefits across various domains, making it an attractive solution for businesses and consumers alike.
Increased Efficiency
IoT enables businesses to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve productivity by automating processes and optimizing resource allocation.
Enhanced Customer Experience
By leveraging IoT, companies can gather valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, allowing them to tailor their products and services to meet individual needs.
Improved Sustainability
IoT promotes sustainable practices by reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and optimizing resource usage. This contributes to a more environmentally friendly and responsible approach to business.
Challenges of IoT
Despite its many advantages, IoT also presents several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its successful implementation and adoption.
Security Risks
As the number of connected devices grows, so does the potential for security breaches and cyberattacks. Ensuring the security of IoT systems is crucial to protecting sensitive data and maintaining user trust.
Interoperability
The lack of standardization in IoT devices and platforms can hinder interoperability, making it difficult for different systems to communicate and work together seamlessly.
Scalability
As IoT networks continue to expand, ensuring scalability becomes a significant challenge. Businesses need to invest in infrastructure and technologies that can support the growing demands of IoT systems.
IoT Security
Security is a critical concern in the world of IoT, as connected devices often handle sensitive data and personal information. Implementing robust security measures is essential to safeguarding these systems and protecting users from potential threats.
Encryption
Encrypting data transmitted between IoT devices and systems is a fundamental security practice. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Authentication
Authentication mechanisms, such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication, help verify the identity of users and devices, preventing unauthorized access to IoT systems.
IoT Privacy
Privacy is another major concern in the IoT landscape, as devices often collect and store vast amounts of personal data. Ensuring user privacy is essential to building trust and encouraging adoption of IoT technologies.
Data Minimization
Data minimization involves collecting only the necessary data for a specific purpose and deleting it once it is no longer needed. This reduces the risk of data breaches and protects user privacy.
Transparency
Being transparent about data collection practices and providing users with control over their data is key to maintaining trust in IoT systems. This includes clear privacy policies and opt-in mechanisms for data sharing.
Future Trends in IoT
The future of IoT looks promising, with several emerging trends set to shape its development and adoption in the coming years.
5G Technology
The rollout of 5G networks will significantly enhance the capabilities of IoT by providing faster speeds, lower latency, and increased connectivity. This will enable more advanced applications, such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing the need for cloud-based solutions and improving real-time decision-making. This is particularly beneficial for IoT applications that require rapid response times.
Artificial Intelligence
The integration of AI with IoT will unlock new possibilities, enabling more intelligent and autonomous systems. This will lead to more personalized and efficient solutions across various industries.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the way we interact with technology, offering numerous benefits and opportunities for innovation. From enhancing efficiency and convenience to promoting sustainability, IoT has the potential to revolutionize industries and improve everyday life. However, addressing challenges such as security, privacy, and interoperability is crucial to ensuring its successful adoption and long-term success.
We invite you to explore the world of IoT further and consider how it can benefit your business or personal life. Don't forget to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and check out our other articles for more insights into the latest trends and technologies in the digital world.